Net Income
Net income is the money left as profits after subtracting all costs and expenses from revenue. It is also called earnings, profits, or "the bottom line."
You calculate net income for a company by starting with revenue, then subtracting all expenses: cost of revenue, operating expenses, interest, taxes, and others.
If revenue is higher than expenses, then net income is positive, and the company is profitable. If expenses are higher than revenue, then it is termed a net loss.
Net income has a similar meaning in personal finance. You calculate it by subtracting tax expenses from an individual's gross (pre-tax) income.
An individual's gross income is the total income before taxes, but net income is what's left after deductions and taxes.
Formulas: calculate net income for a business

There are several different formulas to calculate net income for a company. The simplest one is:
Formula: Net Income = Total Revenue - Total Expenses
You can also calculate net income for a stock by subtracting all the expense items on the company's income statement from the revenue.
Net Income = Total Revenue - Cost of Revenue - Operating Expenses - Depreciation & Amortization - Interest Expense - Taxes - Other Expenses
Because net income is near the bottom of a company's income statement, it is often referred to as the bottom line.
This screenshot shows income statement data from Meta for the past few years:
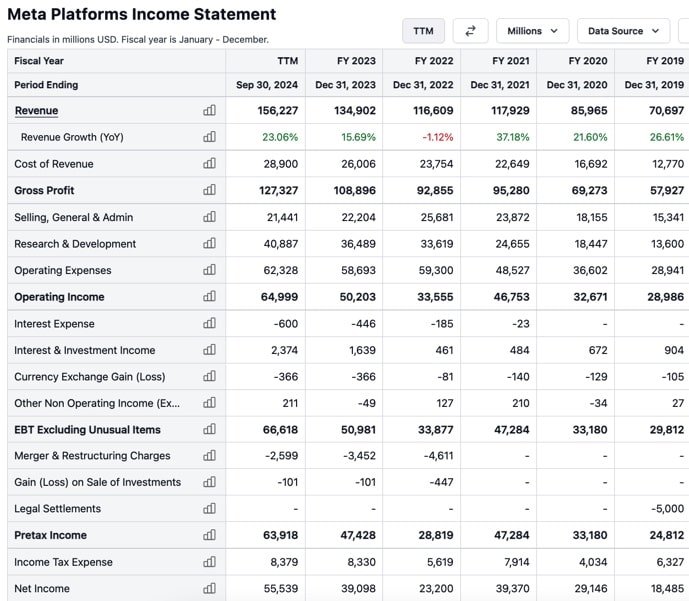
Source: Stock Analysis
As you can see, the revenue (top-line) number is at the top, while the net income (bottom line) number is at the bottom after all expenses have been subtracted.
Net income (profits) can be used for various purposes. These include paying back debt, buying other companies, or returning money to shareholders via dividends and stock buybacks.
The profit margin is closely related to net income. It measures the percentage of the total revenue that is left as profits.
Formula: Profit Margin = (Net Income / Revenue) * 100%
Net income is also used to calculate earnings per share (EPS). This is the profitability metric most closely followed by investors and stock analysts.
Formula: EPS = Net Income / Shares Outstanding
The frequently cited PE ratio can also be calculated using net income, by dividing a company's market cap by the net income in the past 12 months.
Net income can also be used to calculate many other financial metrics and ratios.
Individuals: gross and net income
Gross income for an individual is the total amount of money made from all sources. It is also termed pre-tax income.
Net income for an individual is similar to net income for a business. It is the money left after you subtract all expenses (taxes) from the gross income.
In simple terms, gross income is the total amount of money you make, but net income is what's left after paying taxes.
To get from gross income to net income, you remove deductions from the gross income number and then subtract the taxes.
For example, let's imagine an individual with $50,000 in gross income that qualifies for $5,000 in deductions and has an effective tax rate of 10%.
- Gross Income: $50,000
- Taxable Income: $50,000 - $5,000 = $45,000
- Taxes: $45,000 * 0.10 = $4,500
- Net Income: $50,000 - $5,000 - $4,500 = $40,500
This individual now has $40,500 in net income after subtracting deductions and taxes from a gross income of $50,000.
Gross vs net income for a company
For a company, gross income is also different from net income.
Gross income only subtracts an expense item called "cost of goods sold" or "cost of revenue" from the revenue. These are costs directly related to the production and delivery of the product/service.
On the other hand, net income subtracts all expenses — not just this one expense item.
These are the three most commonly cited income numbers for a company:
- Gross income: Also termed gross profit, this is calculated by subtracting cost of revenue from the revenue.
- Operating income: This is calculated by subtracting cost of revenue and operating expenses from the revenue.
- Net Income: What's left after all costs and expenses have been subtracted.
Here's a screenshot from Apple's income statement data showing gross profit, operating income, and net income.
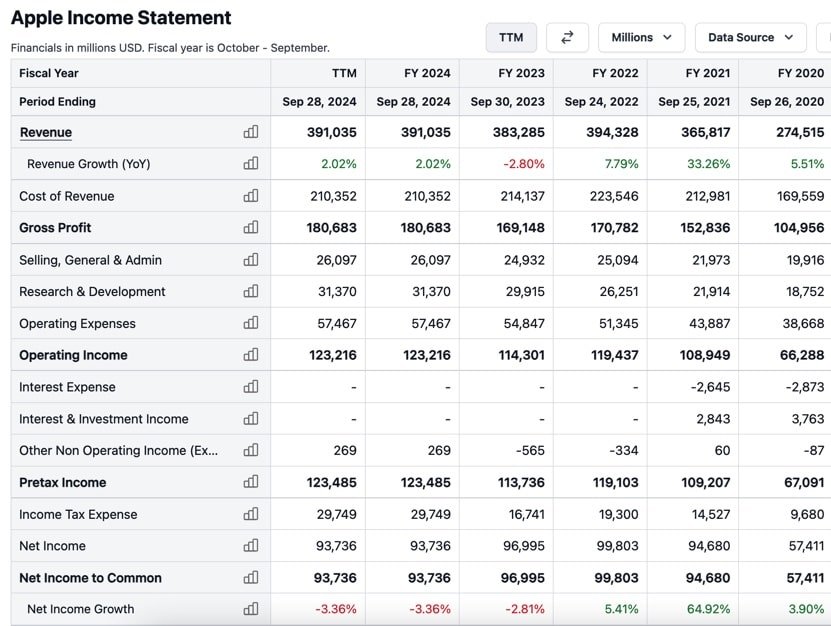
Source: Stock Analysis
As you can see, the "income" number decreases the further you go down the list: Revenue > Gross Profit > Operating Income > Net Income.
Some investors also look at EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) and EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation & amortization). These numbers are similar to net income, except they exclude several expense items.




