What's the Difference Between Revenue and Income?

The difference between revenue and income can be confusing, especially since the terms are often wrongly used interchangeably.
For a company, revenue is the total amount of money received from customers for the sales of products and services.
However, income is what remains after you subtract all costs, expenses, and taxes from the revenue. In other words, income is the same as profits and earnings.
Income = Revenue - Expenses
For an individual, income is the total money earned, including salaries, tips, interest, dividends, and others. The term revenue is rarely used for individuals.
Revenue and income for a company
For a company that makes its money by selling things, the terms sales and revenue are identical and used interchangeably.
As an example, consider a hypothetical business — a grocery store with $100,000 in sales per year.
Out of the $100,000 in revenue, this business needs to pay $40,000 per year for inventory. The business also pays $30,000 in salaries, $10,000 in taxes, and $5,000 in interest on debt.
We can calculate the income this way:
Net Income = revenue - expenses = $100,000 - $40,000 - $30,000 - $10,000 - $5,000 = $15,000
This hypothetical grocery store has a net income of $15,000 on revenue of $100,000, which gives them a profit margin of 15%.
In accounting, revenue is termed the "top line" because it's at the top of the income statement. Net income is called the "bottom line" because it's at the bottom.
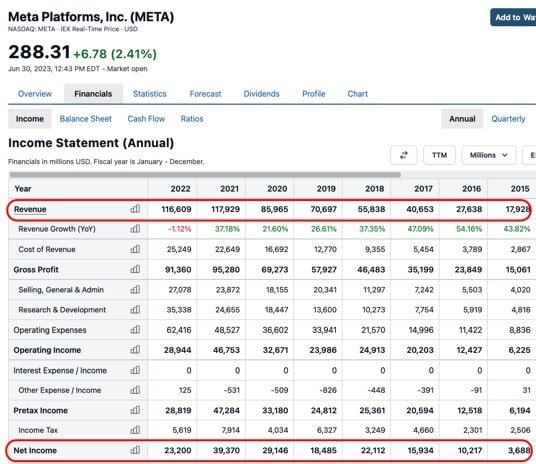
To see the calculation for a real company, here's a screenshot of Facebook's (META) income statement data, highlighting revenue at the top and net income at the bottom:
Income has a different meaning for individuals
For an individual, the term income is used instead of revenue.
As an example, let's imagine a hypothetical person with a $50,000 annual salary.
This person is also a diligent saver and rents out an apartment, collecting $5,000 in dividends per year and $20,000 in rent.
This person's income amounts to:
$50,000 + $20,000 + $5,000 = $75,000 per year
For an individual, total income is also called pre-tax income. After paying taxes, the amount that's left is called net income.
A business has several different types of income
When investors and analysts talk about income for a company, they are usually referring to net income, also termed profits or earnings.
But there are actually several different types of income in business accounting. The main difference between them is which expense categories you subtract from the revenue number.
Here are the three most common income metrics:
- Gross income: Also termed gross profit, this is the amount remaining after "cost of revenue" or "cost of goods sold" has been subtracted from the revenue.
- Operating income: After all operating expenses — such as research and development and selling, general and administrative — have been subtracted from the gross profit.
- Net income: After all expenses, including the cost of revenue, operating expenses, taxes, interest, and others have been subtracted from the revenue.
For most businesses, the number gets smaller the farther you go down on the income statement. Gross profit is lower than revenue, operating income is lower than gross profit, and net income is lower than operating income.
Although net income is the most important, investors and analysts also pay close attention to gross profit and operating income. They can tell you a lot about how different parts of a business are performing.
The investing community often focuses even more on earnings per share (EPS), which is net income divided by the number of shares outstanding. It tells you how much money a company is making for its shareholders.
Companies can grow their net income and EPS by cutting costs, even if revenues are flat or decreasing.
Other types of income often considered include:
- EBIT: Earnings Before Interest & Taxes
- EBITDA: Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation & Amortization
These are similar to net income, except they exclude a few cost items.
The percentage of revenue left as each type of income is called the margin. Commonly watched margins include the gross margin, operating margin, profit margin, EBIT margin, and EBITDA margin.
Generally speaking, when margins are improving, the company is making more money. When margins grow, stock prices tend to go up.
To learn more, check out our full financial term library here.